Android Adapter
Adapters are the link between a set of data and the AdapterView that displays the data.
AdapterView:
- AdapterViews are ViewGroups that display child views given to it by an adapter.
- An example of an AdapterView is a ListView.
- Adapters also provide the child views that display the data in the AdapterView.
- Adapters are responsible for supplying the data and creating the views representing each item.
Adapters get the data and pass it, along with a child view, to the parent AdapterView which displays the child view and the data
The Android Framework has a set of native adapters that are easy to use. You can also create your own custom adapters if you wish.
Two of Android’s common adapters are:
ArrayAdapter:
An ArrayAdapter is an adapter backed by an array of objects. It links the array to the Adapter View.
The default ArrayAdapter converts an array item into a String object putting it into a TextView. The text view is then displayed in the AdapterView (a ListView for example).
- When you create the adapter, you need to supply the layout for displaying each array string. You can define your own or use one of Android’s, such as:
android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1
- There are alternative constructors that you can use for more complex layouts.
- You can also display images instead of strings.
Example coding:
activity_main.xml
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context=".MainActivity" > <ListView
android:id="@+id/list"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" > </ListView> </RelativeLayout>
list_singal.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" > <TableRow> <ImageView
android:id="@+id/img"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"/> <TextView
android:id="@+id/txt"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:textSize="40dp"
android:layout_height="50dp" /> </TableRow> </TableLayout>
MainActivity:
public class MainActivity extends Activity { ListView list; String[] web = { "" + "bird", "boy", "butterfly", "follower", "fruits", "karthi", "nature", "rose" } ; Integer[] imageId = { R.drawable.bird, R.drawable.boy, R.drawable.butterfly, R.drawable.follower, R.drawable.fruits, R.drawable.monkey, R.drawable.nature, R.drawable.rose, }; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); CustomList1 adapter = new CustomList1(MainActivity.this, web, imageId); list=(ListView)findViewById(R.id.list); list.setAdapter(adapter); list.setOnItemClickListener(new AdapterView.OnItemClickListener() { @Override public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> parent, View view, int position, long id) { Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "You Clicked at " +web[+ position], Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } }); } }
CustomList1
public class CustomList1 extends ArrayAdapter<String> { private final Activity context; private final String[] web; private final Integer[] imageId; public CustomList1(Activity context, String[] web, Integer[] imageId) { super(context, R.layout.list_single, web); this.context = context; this.web = web; this.imageId = imageId; } @Override public View getView(int position, View view, ViewGroup parent) { LayoutInflater inflater = context.getLayoutInflater(); View rowView= inflater.inflate(R.layout.list_single, null, true); TextView txtTitle = (TextView) rowView.findViewById(R.id.txt); ImageView imageView = (ImageView) rowView.findViewById(R.id.img); txtTitle.setText(web[position]); imageView.setImageResource(imageId[position]); return rowView; } }
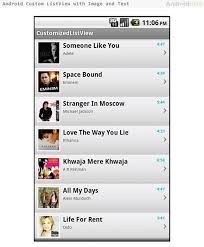
Output:
The SimpleCursorAdapter links the data contained in a Cursor to an Adapter View.
Cursors:
- A cursor is a set of data. You usually get a cursor when you do a database query. The result of your query is contained in the cursor.
- The SimpleCursorAdapter binds the Cursor data to an Adapter View. You define a layout that controls how each row of data is displayed.
- Each row’s view is populated using the column values of the corresponding row in the cursor.
- The SimpleCursorAdapter gets the data out of the Cursor, puts each row of data in a layout that you define and then displays it in the Adapter View.
- When you construct the SimpleCursorAdapter, you specify which column’s data is to be retrieved from the cursor.
- You also specify which fields in your layout are to display this data.
- The adapter then creates a new view for each cursor entry and populates it with the corresponding cursor column values.
Other useful Adapters:
CursorAdapter
- A CursorAdapter links a Cursor’s data to a List View.
- You must include the database’s _id column as it’s used in processing the list item’s selection.
- The SimpleCursorAdapter is a subclass of CursorAdapter.
- The SimpleCursorAdapter is easier to use while the CursorAdapter requires more work but allows more customization.
SimpleAdapter
- The SimpleAdapter links static data to views defined in a layout file.
- You specify the data as an ArrayList of Maps.
- Each entry in the ArrayList will display as a row in a list.
BaseAdapter
- The BaseAdapter is a common base class for an Adapter that can be used in a ListView and a Spinner.
ListAdapter
- The ListAdapter links the data and a ListView displaying the data.
- The List View can display any data type provided it’s wrapped in a ListAdapter.
next we see about Listview.